


Other types of cells, like prokaryotes, don’t have a nuclear membrane surrounding their cellular DNA, which is why mitosis only occurs in eukaryotic cells.
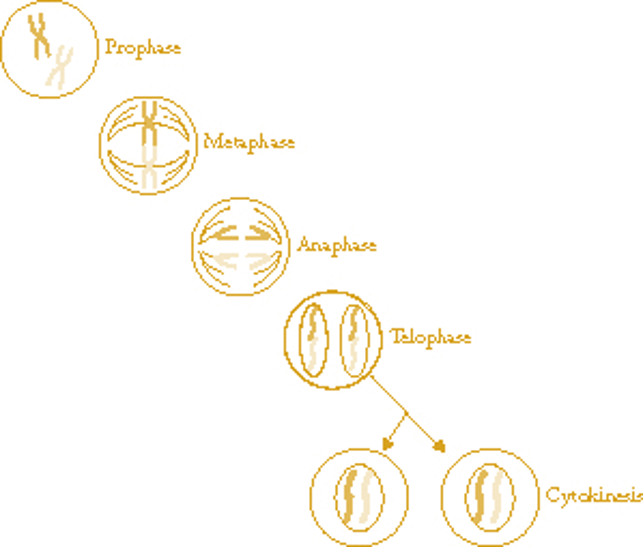
A crucial part of mitosis involves breaking down the nuclear membrane that surrounds the cell’s DNA so that the DNA can be replicated and separated into new cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains the cell’s genetic material. Mitosis occurs in eukaryotic (animal) cells. Mitosis results in two new nuclei-which contain DNA-that eventually become two identical cells during cytokinesis. The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell-known as the “parent cell”-and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis. Mitosis is a process that occurs during the cell cycle. Give you five resources for learning more about the phases of mitosisįeature image: Jpablo cad and Juliana Osorio/ Wikimedia Commons.Provide mitosis diagrams for the stages of mitosis.Break down the four phases of mitosis, in order.Briefly define mitosis and eukaryotic cells.In this article, we’re going to do the following things to break down the four steps of mitosis for you and help you get acquainted with the mitosis phases: The key idea is that the process of mitosis involves four phases, or steps, that you need to understand if you want to understand how mitosis works. In other words, in the world of cell biology, mitosis is kind of a big deal!īut like with anything science-related, mitosis can be sort of confusing when you first try to understand it. This process is vital for maintaining the integrity of the genome and ensuring the proper functioning of the organism.In order to heal an injury, your body needs to replace damaged cells with healthy new ones.and mitosis plays a crucial role in this process! Mitosis is a process of cell division that helps you stay alive and healthy. Overall, the four main stages of mitosis are critical for ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material of the parent cell. A cell plate, also called the cleavage furrow, forms in the middle of the cell, eventually dividing the cell into two. A new nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes, and a new nucleolus forms in each nucleus. This results in the formation of two identical sets of chromosomes, one at each pole of the cell.įinally, during telophase, the fourth and final stage of mitosis, the cell begins to divide into two daughter cells. The mitotic spindle fibers contract, pulling the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. The mitotic spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each chromosome, which is the point at which the two sister chromatids are joined.Īnaphase, the third stage of mitosis, is marked by the separation of the sister chromatids. The mitotic spindle, a network of protein fibers, begins to form and will eventually help to separate the chromosomes during the next stage.ĭuring metaphase, the second stage of mitosis, the chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell, forming a structure called the metaphase plate. The chromatin, which is the DNA and protein material that makes up the cell's genetic material, also begins to condense into visible chromosomes. There are four main stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.ĭuring prophase, the first stage of mitosis, the cell's nucleus begins to condense and the nucleolus disappears. Mitosis occurs in all eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
#PROPHASE STEPS SERIES#
It is a crucial part of the cell cycle, which is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
